Chapter 11 Code#
We begin with some imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numba import njit
Now we recreate figure 11.3. Our first step is to set the parameters.
alpha = 0.6
Q = 2
R = 1
sigma = 0.1 # variance
mu = - sigma**2 / 2
Next we introduce useful functions.
@njit
def wage(k, z):
return (1 - alpha) * (k**alpha) * z
@njit
def theta(w, lda):
if (w < 1 - lda):
return lda / (1 - w)
else:
return 1
@njit
def g(y):
return (y/alpha)**(1/(alpha-1))
@njit
def update(k, z, lda):
" Update the state."
return g(R / (Q * theta(wage(k, z), lda)))
@njit
def a(lda):
return g(R / (lda * Q))
@njit
def generate_ts(lda, init=None, seed=1234, ts_length=10_000):
" Generate a time series from the model."
np.random.seed(seed)
K = np.empty(ts_length)
if init is None:
init = a(lda)
K[0] = init
for t in range(ts_length-1):
z = np.exp(mu + sigma * np.random.randn())
K[t+1] = update(K[t], z, lda)
return K
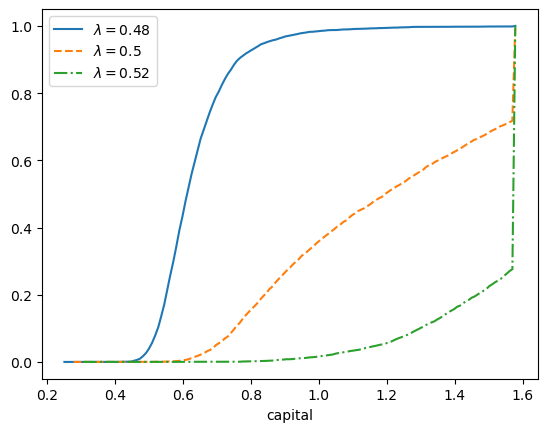
Now we recreate the plot.
b = g(R / Q)
lambdas = 0.48, 0.5, 0.52
line_type = '-', '--', '-.'
mc_size = 5000
grid_size = 150
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for lda, lt in zip(lambdas, line_type):
xvec = np.linspace(a(lda), b, grid_size)
obs = generate_ts(lda, ts_length=mc_size)
def ecdf(y):
return sum(obs <= y) / mc_size
yvec = [ecdf(x) for x in xvec]
ax.plot(xvec, yvec, lt, label=rf'$\lambda={lda}$')
ax.set_xlabel('capital')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
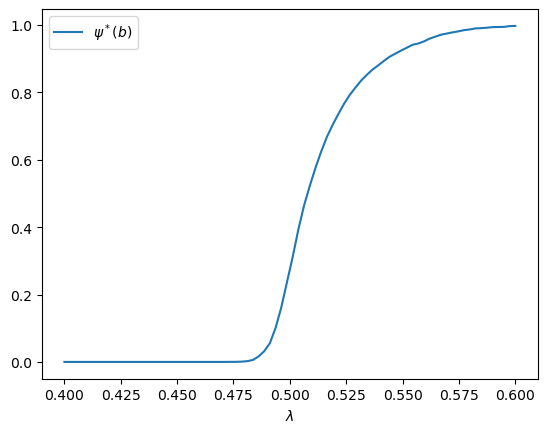
Now we address exercise 11.26.
We need to determine the fraction of time the sample spends at the point \(b\) in the state space over a long horizon, for different values of \(\lambda\).
grid_size = 80
lambdas = np.linspace(0.4, 0.6, grid_size)
mc_size = 5000
prob_at_b = np.empty_like(lambdas)
for i, lda in enumerate(lambdas):
obs = generate_ts(lda, ts_length=mc_size)
prob_at_b[i] = np.mean(obs == b)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(lambdas, prob_at_b, label=r'$\psi^*({b})$')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\lambda$')
ax.legend()
plt.show()